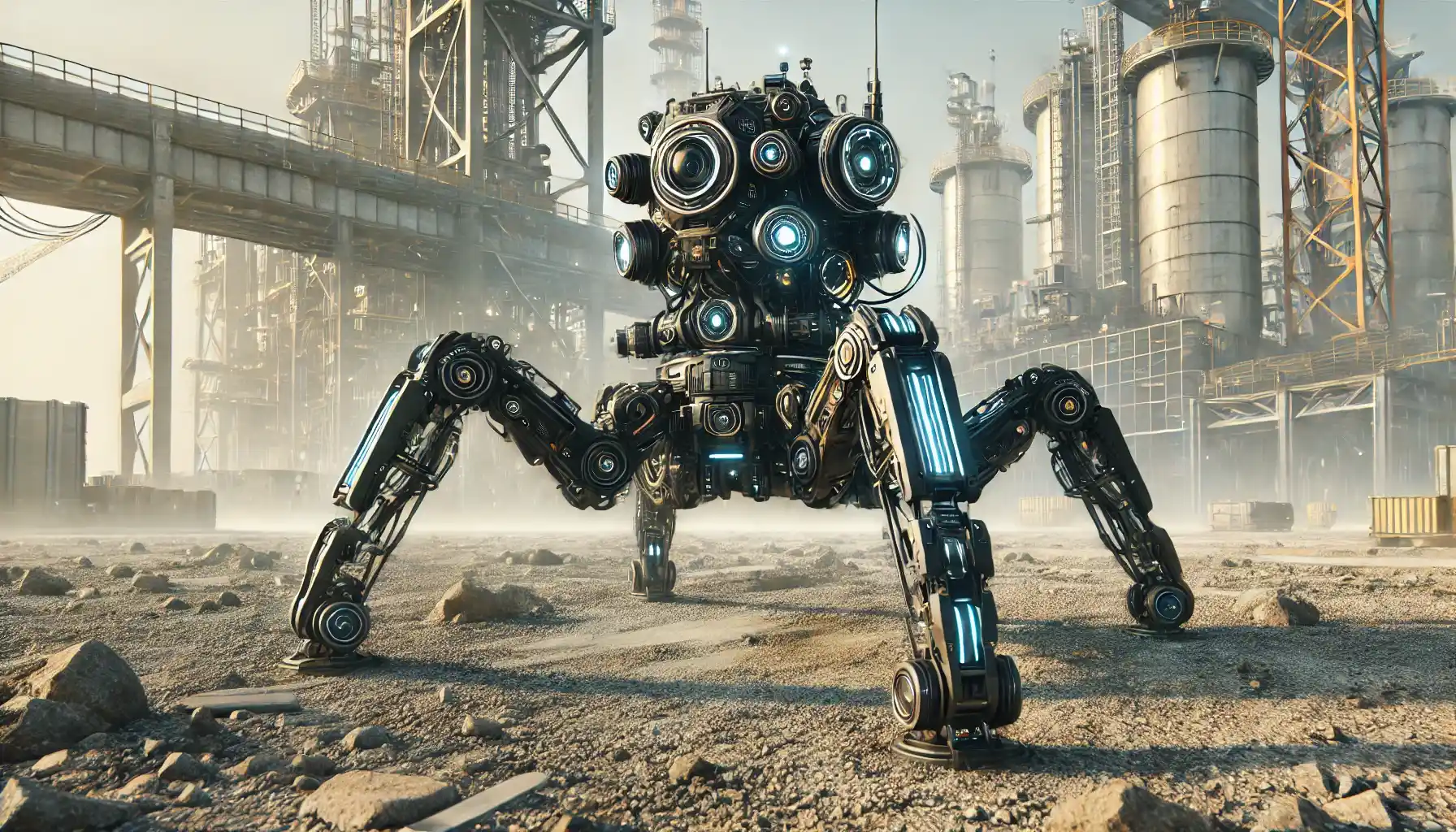
In our rapidly evolving technological landscape, one particular innovation is capturing the imagination of both engineers and enthusiasts alike: the spider robot. These remarkable machines are modeled after one of nature’s most efficient and agile creatures—the spider. But what exactly makes a spider robot so special, and how are these multi-legged wonders shaping the future of robotics, automation, and beyond? In this article, we’ll examine what a spider robot is, explore its wide range of applications, and discuss the challenges and future prospects of this exciting field.
What Is a Spider Robot?
Before diving into the impact of this fascinating technology, it’s important to understand what a spider robot actually is. As the name suggests, a spider robot is a type of robotic device that mimics the form and movement of a spider—typically featuring multiple legs (often eight, though sometimes fewer) arranged symmetrically around a central body. These legs enable superior mobility, allowing the robot to move in ways traditional wheeled or tracked machines cannot.
Unlike conventional robots that rely on wheels for motion, spider robots can climb, crawl, and maneuver across uneven surfaces with relative ease. This unique mobility is what makes them ideal for tasks in challenging terrains—whether it’s navigating rough outdoor environments or moving through confined indoor spaces. The spider robot’s design also spreads its weight across multiple contact points, reducing the pressure on any single leg and often allowing for a more stable, balanced gait.
The Science Behind Spider-Like Movements
Leg Mechanisms and Degrees of Freedom
A spider robot’s agility largely comes from its legs. Each leg can include multiple joints, often referred to as “degrees of freedom.” The more joints a leg has, the more ways it can twist, turn, and adapt its stance to a given surface. For instance, a spider robot with three or more degrees of freedom per leg can tackle inclines, declines, or even vertical walls (in some advanced cases).
Moreover, these robots usually employ sophisticated control algorithms to coordinate all legs seamlessly. Think of how a real spider moves—each leg shifts in perfect harmony with the others. In the same way, the robot’s onboard controllers or external programming ensure every movement is balanced and efficient.
Sensors and Feedback Systems
Advanced spider robots go beyond mechanical dexterity by integrating various sensors—like gyroscopes, accelerometers, and proximity sensors—to understand their surroundings. This sensor data is fed back into the control system, allowing the robot to adjust its speed, direction, or stability in real time.
In many cases, the spider robot is also equipped with cameras or LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems to map its environment three-dimensionally. This mapping capacity not only helps avoid obstacles but also supports tasks like exploration, inspections, and search-and-rescue missions.
Innovative Applications of this Robots
Spider robots are not just science-fiction curiosities—they are becoming critical tools in various industries. From manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and research, the versatility of these multi-legged machines is unlocking new possibilities.
Manufacturing and Automation
One of the earliest arenas to embrace the spider robot was manufacturing. Factories and warehouses are constantly seeking more agile and flexible systems to optimize their operations. Traditional industrial robots, often bolted to the floor, excel at repetitive tasks but can lack mobility. Spider robots, however, bring a new level of flexibility to the assembly line. Their ability to navigate cluttered environments, climb over or under obstacles, and adapt to changing layouts makes them invaluable in a constantly evolving manufacturing space.
For instance, these robots can handle tasks like parts inspection, quality control, and material handling in spaces where traditional robots might struggle. Additionally, some spider robots are equipped with grippers or specialized tools at the end of one or more legs, helping them perform intricate tasks like picking, placing, or welding components with improved precision.
Transportation and Warehousing
In the logistics sector, speed and efficiency are paramount. As e-commerce continues to grow, warehouses are scaling at a rapid pace, often with aisles packed tightly with products and shelves. A spider robot’s ability to climb or step over clutter can be a game-changer, eliminating the need for large open spaces that standard wheeled robots require.
Moreover, these robots can be deployed for inventory management by scanning barcodes on products stored in high or hard-to-reach places. Their camera systems can also identify damaged packaging or other issues, relaying this information to a central control system so that humans can take corrective measures. Over time, spider robots can continuously map the warehouse layout, spotting changes or reorganizations that might be missed by other automated systems.
Infrastructure Inspection
From towering bridges to long pipelines, infrastructure requires regular inspection to ensure public safety. The challenge lies in reaching and thoroughly examining those difficult-to-access areas. This is where the spider robot shines. With its spider-like legs, it can crawl over beams, girders, or pipelines, capturing high-resolution images, ultrasonic readings, or even thermal scans to detect cracks, corrosion, or weaknesses. This reduces the need for human inspectors to scale potentially dangerous heights or crawl through cramped passages. By automating the inspection process, spider robots make it faster, safer, and more comprehensive.
Search and Rescue Missions
In disaster-stricken environments—like earthquake zones or collapsed buildings—time is of the essence. The innate ability of a spider robot to traverse rubble-strewn landscapes makes it an ideal candidate for search and rescue missions. Equipped with night-vision cameras, thermal imaging, and even microphones to pick up faint sounds, spider robots can move quickly through unstable areas, locating survivors without putting rescue personnel at risk. This rapid response capacity can literally save lives, making these robots an invaluable addition to emergency teams worldwide.
Healthcare and Medical Research
Though less common than in industry, spider robots are also making strides in healthcare. Miniaturized versions of spider-like robots have been proposed for minimally invasive surgical procedures. These micro-scale spider robots could, in theory, crawl through the human body—guided by imaging technologies—to deliver medicine or perform targeted biopsies. While many of these applications are still in the research phase, the potential to reduce surgical trauma and speed up recovery times is vast.
Challenges in the Spider Robot Ecosystem
Despite their many advantages, spider robots also face significant challenges. For one, building a multi-legged robot that can coordinate complex movements requires advanced hardware and software. The mechanical joints must be durable enough to handle repeated stresses, and the computational systems must process sensory data and control algorithms in real time.
Power Supply and Efficiency
One critical issue is power consumption. More legs mean more motors, and more motors mean more energy usage. This is especially problematic when considering battery life—something that’s vitally important in mobile robots. Engineers are constantly experimenting with lighter materials and more efficient motor designs to extend operational time.
Cost and Scalability
Manufacturing spider robots remains expensive, given the intricacy of their mechanical and electronic systems. Prototyping alone can be costly, and mass production isn’t as straightforward as churning out simple, wheeled robots. However, as 3D printing and other manufacturing technologies become more advanced, the cost barrier is expected to come down, potentially making spider robots more accessible to a wider range of industries.
The Future
It’s evident that spider robot technology has enormous potential, but where do we go from here? Many experts predict an increased shift towards collaborative robots—sometimes called “cobots”—that work alongside humans. Spider robots, with their agility and adaptability, could be invaluable partners on factory floors, construction sites, and research labs.
Additionally, advancements in artificial intelligence will continue to improve the robot’s decision-making processes. As machine learning algorithms become more sophisticated, spider robots could learn from past failures, adapt to changing conditions, and fine-tune their movements. This self-learning capability could lead to breakthroughs in autonomy, allowing them to perform tasks with minimal human oversight.
Embracing the Spider Robot Revolution
The world is only beginning to scratch the surface of what these remarkable machines can do. From industrial manufacturing to search and rescue, the spider robot is pushing the boundaries of innovation, making life safer, easier, and more efficient. As we look to the future, we can expect continuous improvements in design, energy consumption, and cost, eventually propelling spider robots into the mainstream.
For anyone interested in robotics, the spider robot is a captivating example of bio-inspired engineering. By mimicking nature’s tried-and-tested designs, robotics experts have unlocked new possibilities that could transform the way we live and work.
Want to learn more? Check out this authoritative resource on robotics and emerging technology for additional insights.